Learn, Build, Apply
Welcome to our scientific blog — a growing collection of free, hands-on resources dedicated to geospatial analysis, machine learning, blockchain, IoT, and urban data science. Whether you’re just starting out or already working in the field, you’ll find a wide range of practical tutorials, code snippets, and step-by-step guides. These materials are designed to help you explore, apply, and extend tools such as Python, Solidity, QGIS, R, Jupyter, and more — all in the context of real-world spatial challenges.
From Large Language Models to Autonomous AI Agents — Architecture, Capabilities, and Emerging Risks
arge Language Models are stateless, single-pass prediction engines — powerful but passive. Wrapping them in a perception–action loop with environment access and tool use transforms them into something qualitatively different: autonomous AI agents. This post walks through the transformer architecture (embeddings, self-attention, likelihood, checkpoints, contextual memory), explains how the agent paradigm introduces closed-loop reasoning over environments and tasks, surveys the growing toolkit ecosystem (LangChain, AutoGPT, OpenClaw, Claude Code), and examines the emerging risk landscape — from social-agent platforms like Moltbook to physical-world interfaces like Rent a Human, where agents can coordinate human workers across compartmentalized tasks that no single participant can see as part of a larger plan.
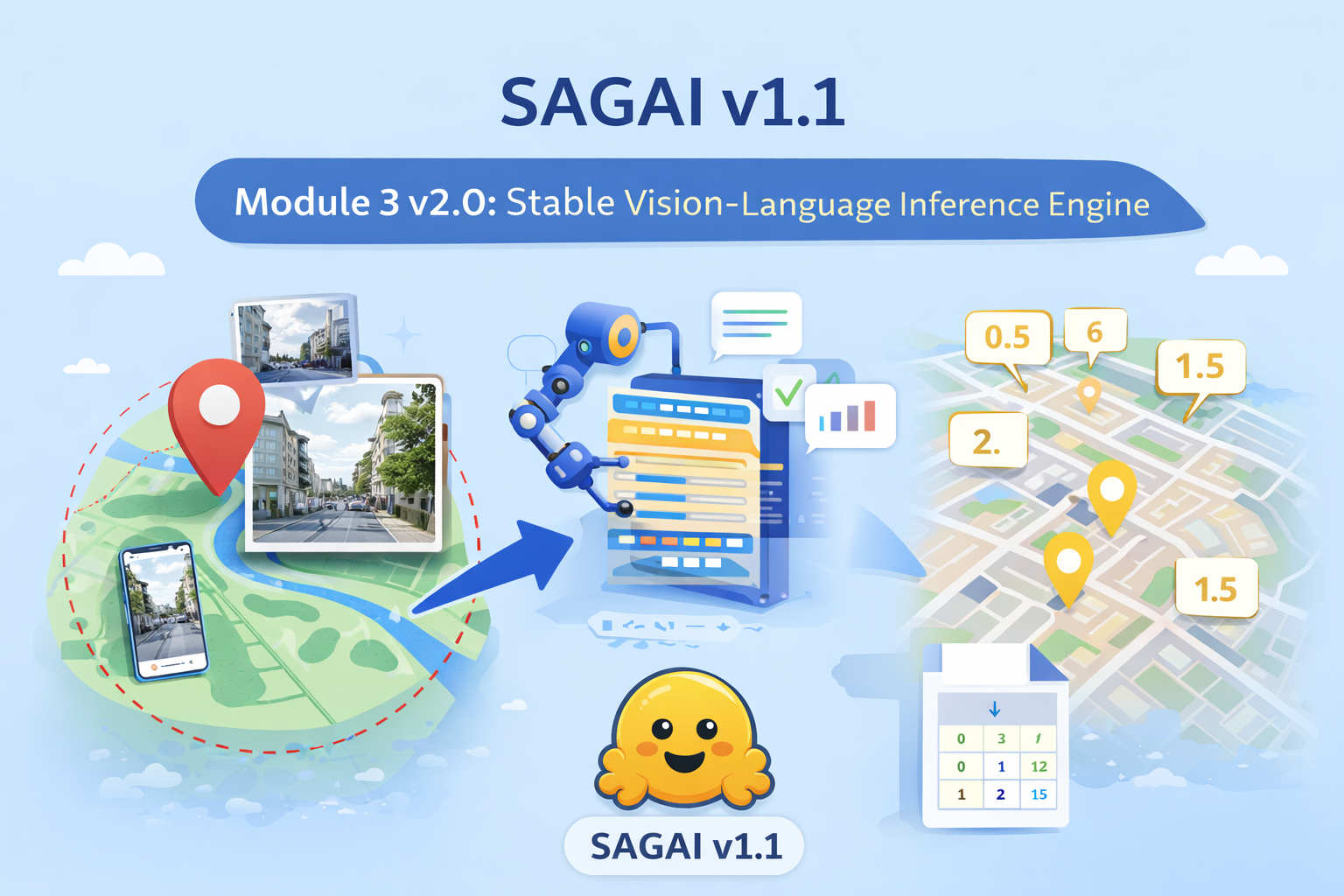
A Stable and Reproducible Vision–Language Inference Engine for SAGAI v1.1
SAGAI v1.1 introduces Module 3 v2.0, a stable and reproducible vision–language inference engine for streetscape analysis. Built exclusively on Hugging Face LLaVA models, it enables robust multimodal processing of street-level images for large-scale urban and geospatial analysis.
Qwen Image Edit for Urbanism v1.3 — Mask-Controlled Editing With Prompt or Reference Guidance
Version 1.3 of Qwen Image Edit for Urbanism introduces mask-controlled editing in ComfyUI, enabling precise, localized image transformations using prompts or reference images. The new Grow Mask utility softens boundaries, preserves unmasked areas, and integrates seamlessly with existing single-image and sequential workflows.
Deploy a Guest Book on an EVM Blockchain Using Remix
Learn how to deploy your first smart contract on an Ethereum-compatible blockchain using Remix and the Sepolia testnet. In this beginner-friendly guide, we build a simple on-chain guestbook, connect MetaMask, verify the contract on Etherscan, and interact with it directly through the blockchain. A perfect starting point for anyone curious about smart contracts, Solidity, and decentralized applications.
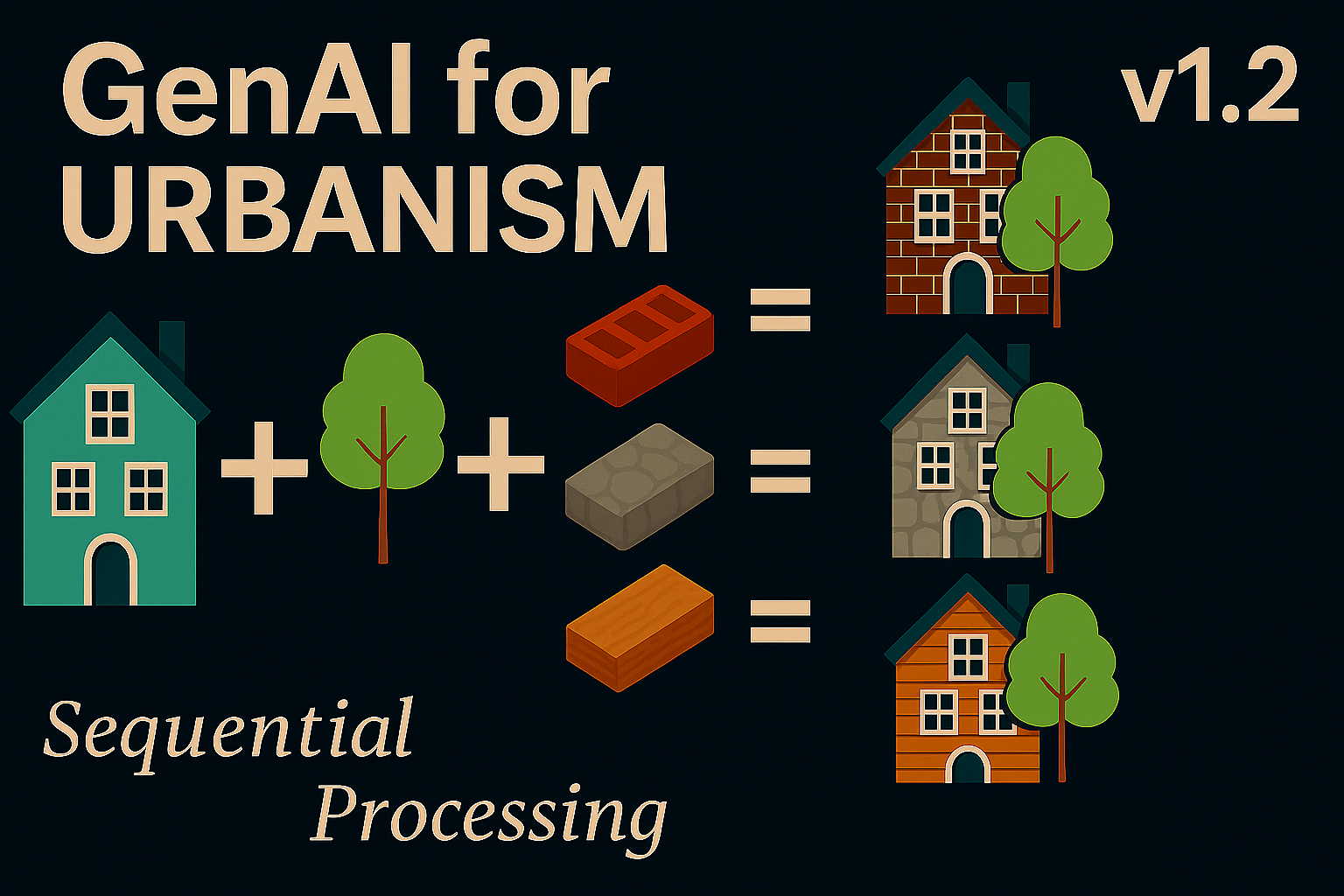
Qwen Image Edit for Urbanism v1.2 — Custom Nodes & Sequential Processing
ComfyUI Sequential Image Editing for Urbanism arrives in Qwen v1.2 with custom Python nodes, multi-image batch processing, and a six-slot buffer for reproducible urban edits. This version streamlines automated workflows for researchers, designers, and architects working with street and neighborhood imagery.
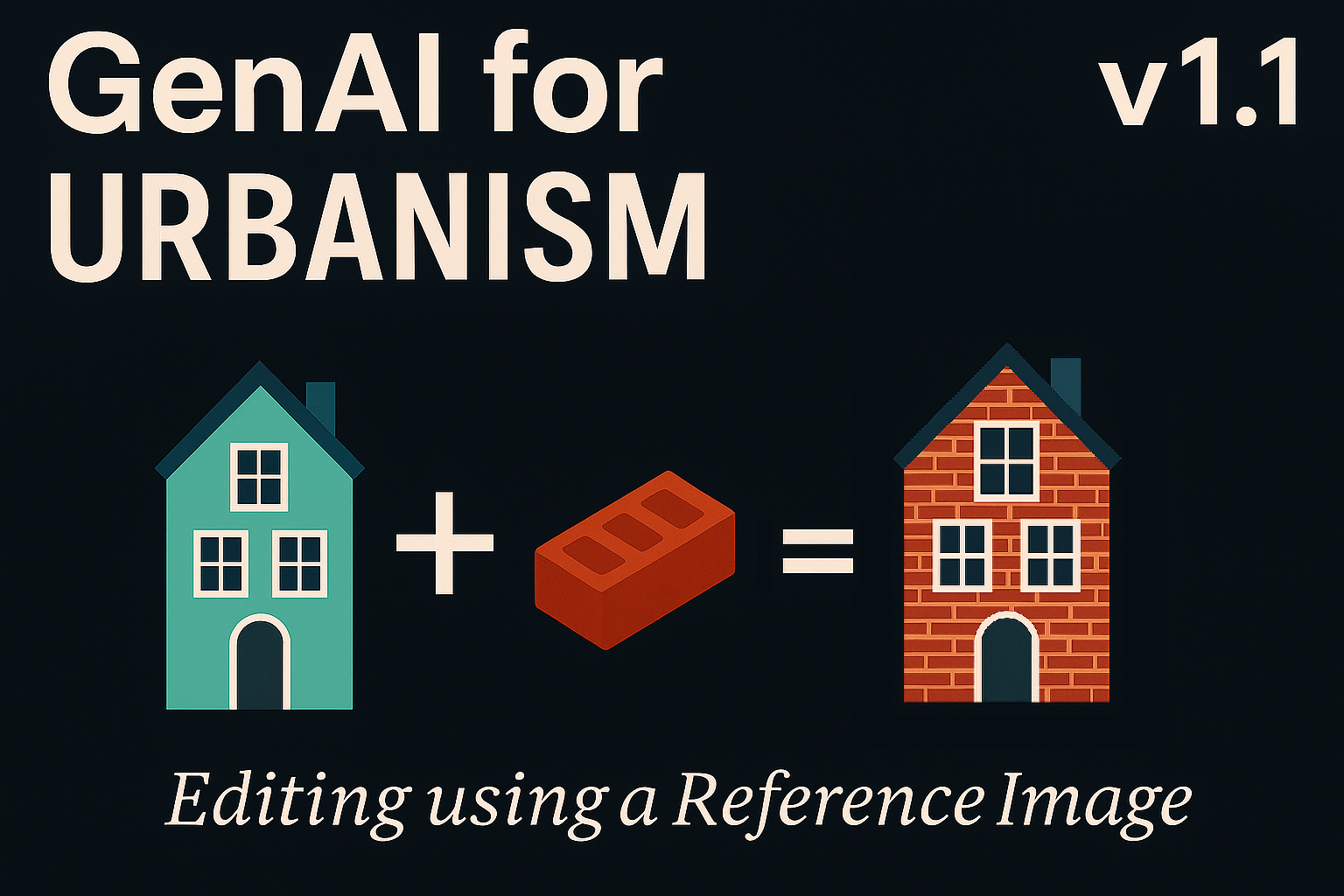
Qwen Image Edit for Urbanism v1.1 — Editing using a Reference Image and Advanced Sampling
Qwen Image Edit for Urbanism v1.1 expands local AI editing in ComfyUI with advanced sampling and dual-image workflows. The new Lightning LoRA system improves realism, texture fidelity, and processing speed, enabling fast, privacy-preserving urban scene transformation—entirely offline.
Qwen Image Edit for Urbanism v1.0 — Building a Qwen Pipeline in ComfyUI
Learn how to build a fully local AI image-editing workflow for urbanism and architectural visualization using ComfyUI and Qwen-Image-Edit. This step-by-step guide runs entirely offline with GGUF models, providing fast, private, and realistic visual edits.
Getting Started with MetaMask and the Polygon Amoy Testnet
Learn how to configure MetaMask for the Polygon Amoy testnet, claim free POL tokens and verify your transactions. Beginner‑friendly guide.
Processing Spatial Data in the Cloud with GeoPandas and Google Colab
Learn how to process geospatial data entirely in the cloud using GeoPandas, Google Colab, and Drive. Create, analyze, and save maps without local setup.
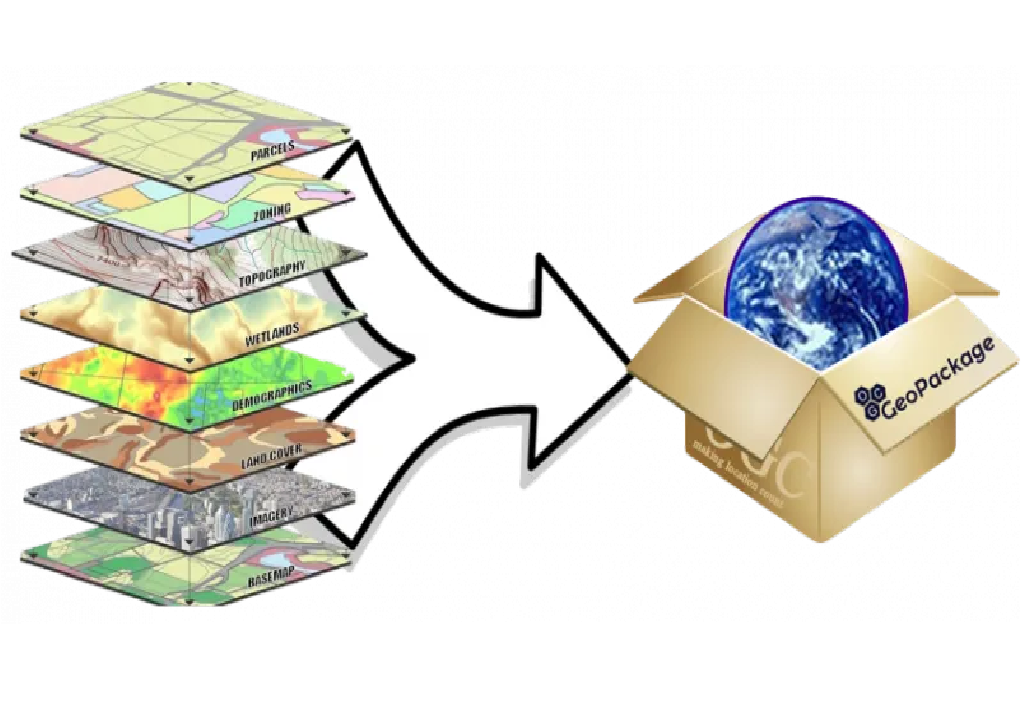
How to import a GeoPackage layer in Python (geopandas) and R (sf)
GeoPackage is an open and non-proprietary data format that allows different layers to be stored within the same file. In this post, we are going to read and save layers using python (geopandas) and R (sf).
Install R and RStudio for Spatial Analysis
R is an open-source statistical programming language used in statistical analysis but also in spatial analysis, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) applications. In this guide, we will walk you through the initial steps of setting up R and RStudio along with installing essential packages and testing them with spatial data.
Controlling QGIS with Python using the Jupyter Notebook
Have you ever wondered about controlling QGIS with a Python script ? In this blog post, we'll explore how to call QGIS from a Python script in the Jupyter Notebook.
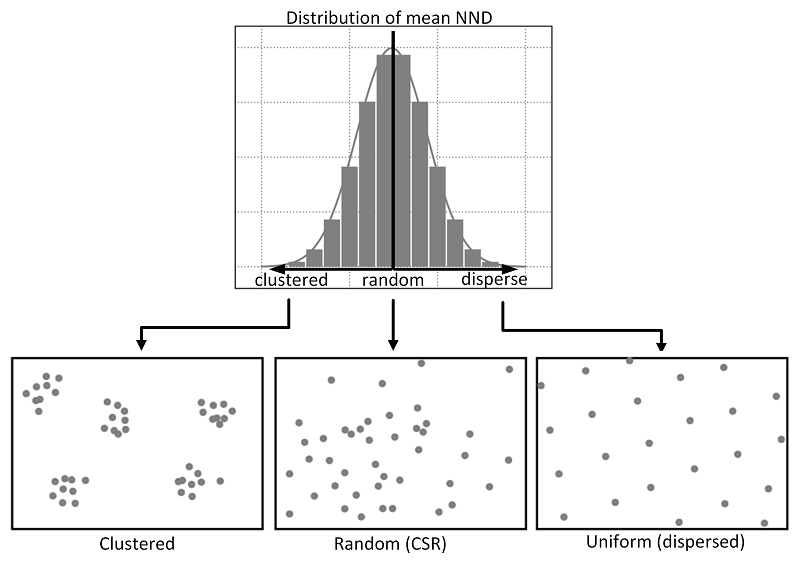
Exploring Spatial Patterns of Point Distributions using NDD and CSR
Calculating Nearest Neighbor Distance (NND) and comparing it with Complete Spatial Randomness (CSR) can be useful in various fields. In this tutorial, we will see together how to calculate a nearest neighbor distance from a given point pattern and compare it to a random distribution (CSR).
Getting Started with Python using Anaconda and Jupyter Notebook
In this guide you'll find clear instructions on setting up Python with Anaconda for spatial analysis. Then, we'll cover installing Python alongside Anaconda and adding essential dependencies like GeoPandas via the Anaconda Prompt. Lastly, we'll explore using the Jupyter Notebook for practical application.