
Highlights
- Deploy Your First Smart Contract: Learn how to publish a simple on-chain guestbook to an Ethereum testnet using Remix, the browser-based IDE for Solidity.
- Connect MetaMask to Sepolia: Add the Sepolia test network to MetaMask, get free test ETH, and prepare your wallet for deployment.
- Interact On-Chain via Etherscan: Write messages to the blockchain, read stored data, and understand how smart contracts expose transparent read/write functions.
Have you ever wanted to experiment with blockchain development but didn’t know where to start? In this beginner-friendly tutorial, we’ll guide you through deploying your very first smart contract on a blockchain testnet using Remix, an in-browser IDE designed for Ethereum-compatible chains. Whether you’re curious about decentralized applications (dApps), NFTs, or simply want to see how code becomes blockchain logic, this guide will get you started — no prior blockchain experience required.
1.Introduction
What is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing program that runs on a blockchain. It stores logic and rules in code — such as sending tokens or recording data — and once deployed, it executes automatically when conditions are met. Smart contracts are immutable (can’t be changed once deployed) and transparent, making them ideal for decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chains, governance, and more. Solidity is the main programming language used to write smart contracts for Ethereum. It is a statically typed, contract-oriented language designed specifically for blockchain logic and storage. Because Solidity compiles to EVM bytecode, the same contract can run on any EVM-compatible blockchain — including Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, Avalanche, BNB Chain, and many others.
What is Remix and Why Use It?
Remix is a web-based Integrated Development Environment (IDE) designed specifically for writing, testing, and deploying smart contracts in the Solidity programming language. One of its biggest advantages is that it requires no installation or setup — everything runs directly in your browser. Remix integrates seamlessly with MetaMask and supports deployment to Ethereum-compatible testnets like Goerli and Polygon Amoy. It also offers a powerful set of tools for compiling, debugging, and interacting with your contracts, making it an ideal choice for both beginners and experienced developers.
2. Connect to Sepolia Testnet
Before deploying a smart contract, you need a wallet connected to an Ethereum test network. If you’re new to MetaMask, start with our beginner guide here:
👉 Getting Started with MetaMask and the Polygon Amoy Testnet
(Use the same installation steps — MetaMask works the same for all EVM chains.)
Once MetaMask is installed and your wallet is set up, you can add the Ethereum Sepolia Testnet. Sepolia is Ethereum’s primary development and testing network. It behaves like mainnet, but uses test ETH (fake ETH) that you can request for free from faucets. Sepolia is ideal for learning and testing smart contracts because it behaves almost exactly like Ethereum mainnet. It mirrors the same architecture, gas mechanics, and transaction flow, which means everything you deploy or test on Sepolia works the same way on Ethereum. Developer tools such as Remix connect to it directly, and because Sepolia is widely supported, stable, and fast, it has become the standard environment for Ethereum development and education. Since Solidity compiles to EVM bytecode, contracts you deploy on Sepolia behave exactly like they will on Ethereum mainnet.
To add Sepolia manually:
-
Open MetaMask
-
Click Add network → Add a network manually
-
Enter the following Sepolia settings:
Network Name: Ethereum Sepolia
New RPC URL: https://rpc.sepolia.org
Chain ID: 11155111
Currency Symbol: ETH
Block Explorer URL: https://sepolia.etherscan.io
Your MetaMask screen should now show the Sepolia network, ready to use. Once saved, you’ll be connected to the Ethereum Sepolia Testnet and can interact with dApps, deploy contracts from Remix, and send test transactions with no real-world cost. Just like Polygon’s Amoy testnet requires test POL tokens, Ethereum Sepolia requires test ETH to pay for transactions. You can get free Sepolia ETH from multiple faucets. I recommend using this one https://sepolia-faucet.pk910.de/
3. Prepare your Smart Contract
Now that MetaMask is connected to Sepolia, we can look at the smart contract we’ll deploy. Below is a minimal “GoldenBook” contract written in Solidity. It’s a simple on-chain guestbook: anyone can write a message, and the contract stores it permanently on the blockchain. Messages are saved along with the sender’s address and the time they were submitted, and the contract provides a function to retrieve everything that has been written so far.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT pragma solidity ^0.8.20; /// @title GoldenBook - A minimal on-chain guestbook (livre d'or) contract GoldenBook { // Simple structure to store a message struct Message { address author; // who sent it string content; // the message text uint256 timestamp; // when it was written } // All messages stored on-chain Message[] private messages; /// @notice Add a new message to the guestbook /// @param content The text to save permanently on-chain function postMessage(string calldata content) external { require(bytes(content).length > 0, "Message cannot be empty"); messages.push(Message({ author: msg.sender, content: content, timestamp: block.timestamp })); } /// @notice Retrieve all messages in the guestbook /// @return An array of Message structs function getAllMessages() external view returns (Message[] memory) { return messages; } }
This contract begins with a simple data structure called Message, which stores who wrote the message, what they wrote, and when they wrote it. All messages are kept in an array called messages, which is stored permanently on-chain. The postMessage function allows anyone to add a new entry; it checks that the message isn’t empty, then records the sender’s address, the text, and the current timestamp. The getAllMessages function returns the full list of stored messages and is marked as a view function, meaning it doesn’t change blockchain state and costs no gas to call. Altogether, this small contract demonstrates the core ideas of Solidity: defining data, writing functions that change state, and exposing read-only views for external applications.
4. Deploy using Remix
With your contract ready and MetaMask connected to the Sepolia testnet, the next step is to deploy it on-chain. The easiest way to do this is with Remix, Ethereum’s browser-based development environment. Remix allows you to compile your Solidity code, connect directly to MetaMask, and publish your contract to the blockchain in just a few clicks.
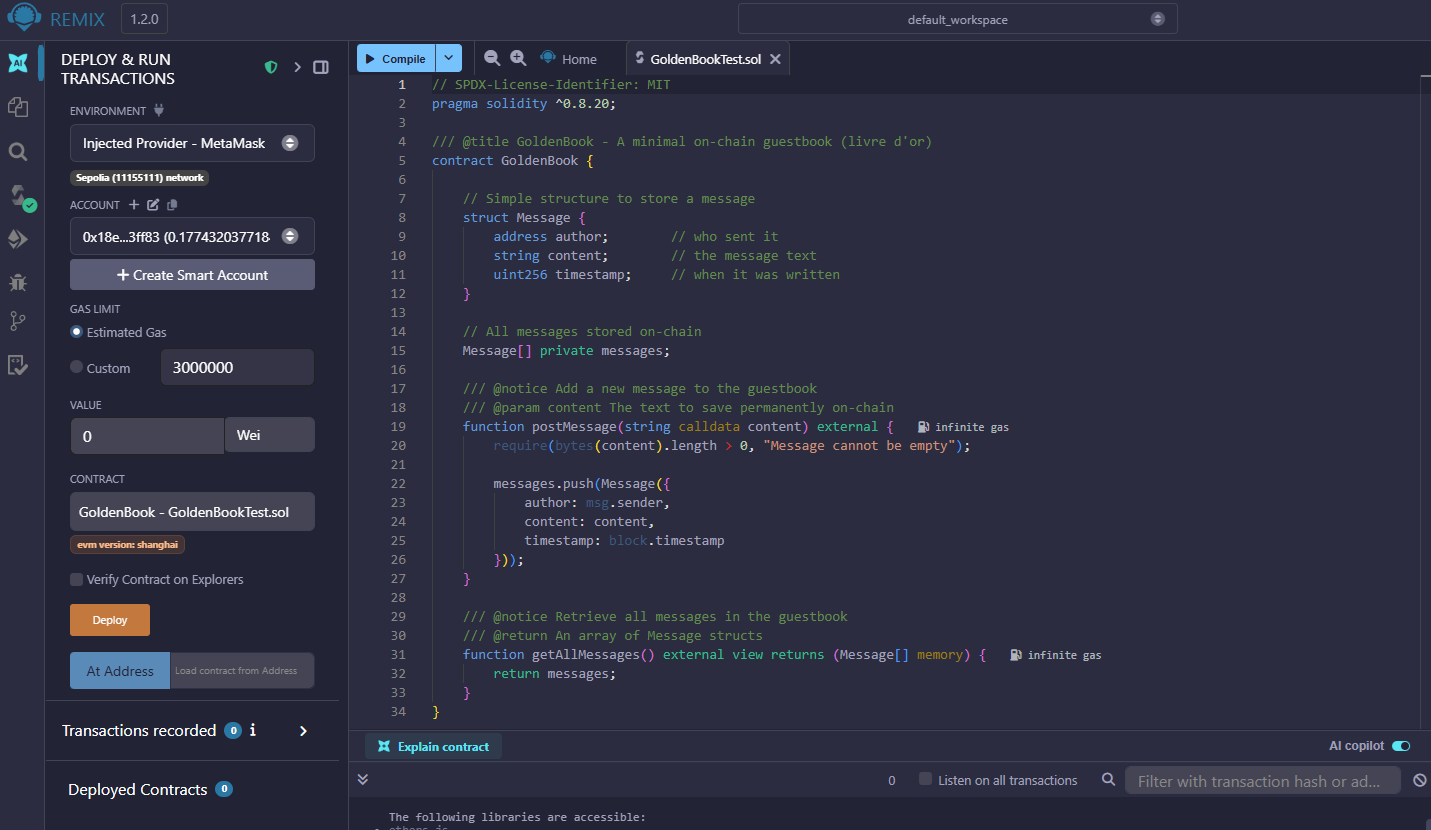
Start by opening Remix at https://remix.ethereum.org and creating a new file called GoldenBook.sol, then paste the contract code from the previous section. Once the file is ready, open the Solidity Compiler tab and select the matching compiler version (in this case, 0.8.20). Press Compile to generate the contract bytecode. Remix will instantly show whether the code is valid and ready for deployment.
After the contract compiles successfully, switch to the Deploy & Run Transactions panel. In the “Environment” dropdown, select Injected Provider (MetaMask)—this tells Remix to use the Sepolia network already configured in your MetaMask wallet. Your MetaMask extension will prompt you to connect Remix if it’s the first time. Once connected, ensure that the selected account has Sepolia ETH and that “GoldenBook” appears in the contract selector. Click Deploy, confirm the transaction in MetaMask, and wait for it to be included in a block. You’ll see the deployed contract appear in Remix under “Deployed Contracts,” along with your transaction hash.
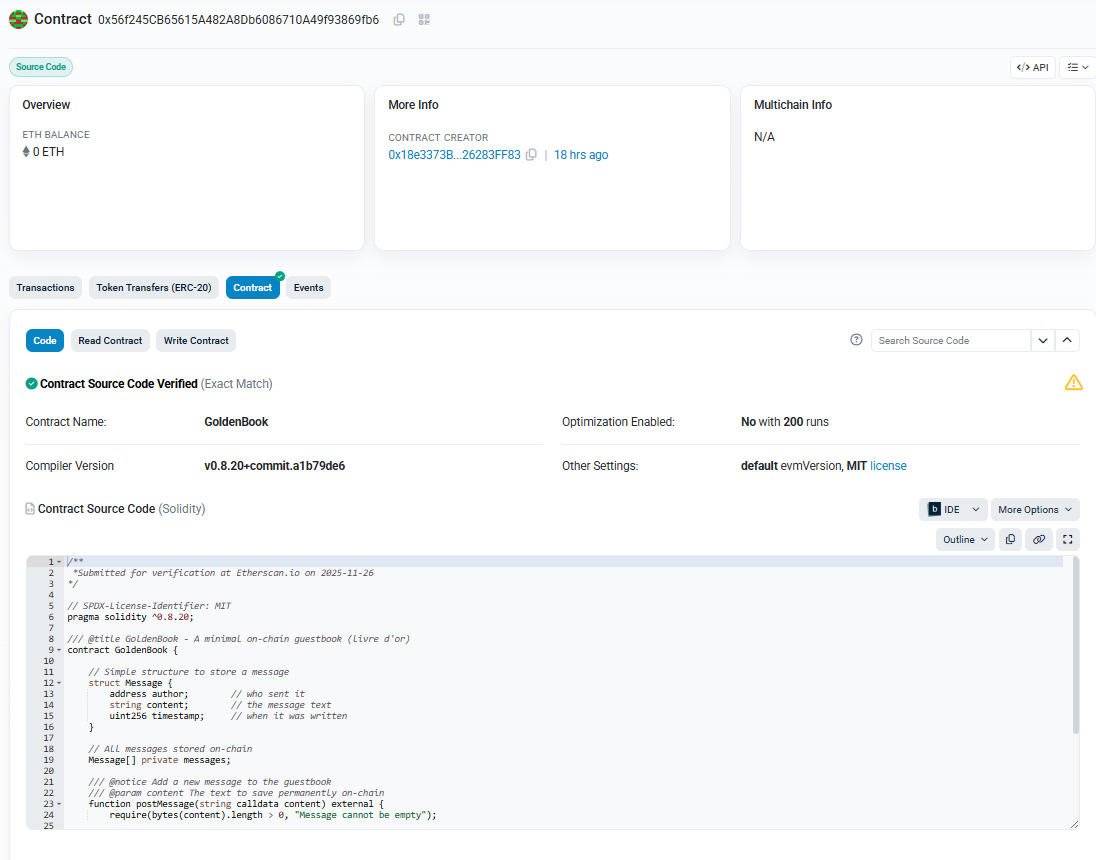
At this point, your contract is live on the Sepolia blockchain, but there’s one last step that is highly recommended: verifying your contract on Etherscan. Verification publishes your Solidity source code alongside the deployed bytecode, allowing anyone to inspect, review, or interact with your contract directly from the explorer. This matters because a blockchain contract is transparent by nature—verification proves the code you shared publicly is the same code deployed on-chain, which builds trust and makes your guestbook readable from tools like Etherscan’s contract tab. It also helps with debugging, audits, and integrating with frontends later on.
Once the contract is compiled and deployed through Remix, you can click “View on Etherscan” in the Remix console to inspect the transaction. On the Etherscan page, click the “To” field of the transaction to open your newly deployed contract address. This brings you to the contract’s dedicated page, where you can verify the source code. Verification requires selecting the correct compiler version, license identifier, and pasting your Solidity source code exactly as deployed. For simple contracts like our GoldenBook, you can paste the code directly since it lives in a single file. For more advanced projects—especially those using imports, libraries, or frameworks—you often need to flatten the contract so all the dependent files are merged into one before verification.
Once submitted, Etherscan will match the compiled bytecode with your source code. A successful verification makes your contract’s code readable on-chain and unlocks the “Read” and “Write” tabs, allowing anyone to interact with it directly from the explorer. You can also view the contract deployed in this tutorial at https://sepolia.etherscan.io/address/0x56f245CB65615A482A8Db6086710A49f93869fb6, although testnets sometimes reset, so the contract may no longer exist by the time you read this.
5. Write and Read the Guest Book (Interact with the Smart Contract)
Now that the contract is verified on Etherscan, you can interact with it directly from your browser. When you open the contract page, you’ll see several tabs, including Read Contract and Write Contract. These act as a simple interface for calling the functions you created in your Solidity code.
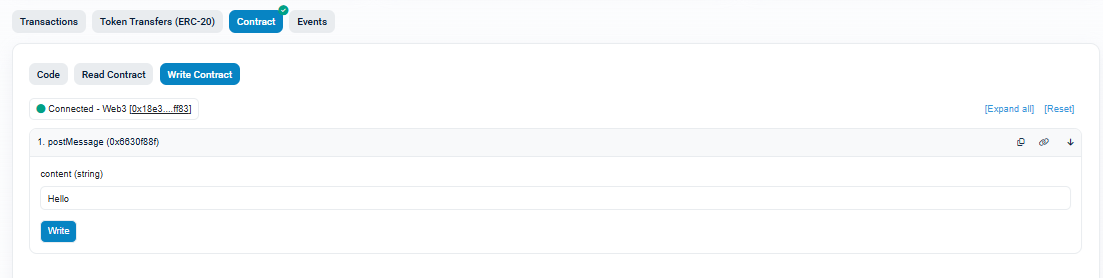
To add a new entry to the guestbook, go to the Write Contract tab, as shown in the figure below. Before sending a message, click “Connect to Web3” so Etherscan can link to your MetaMask wallet on the Sepolia network. Once connected, open the postMessage section, type your message, and submit the transaction. MetaMask will ask you to confirm—it needs to do this because writing a message modifies the blockchain and therefore requires gas. After confirming, wait a few seconds for the transaction to be mined. Your message is now permanently stored on-chain.
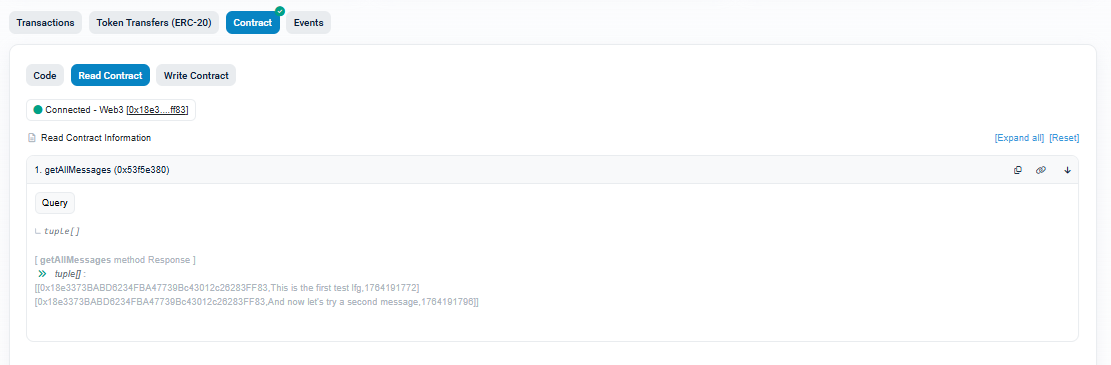
To view what has been written so far, switch to the Read Contract tab. This interface lets you call read-only functions such as getAllMessages without paying any gas, as shown in the next figure. Because read calls do not modify the blockchain, they can be executed instantly and for free. When you click getAllMessages, Etherscan will return the full list of stored messages, including the sender address and timestamp for each entry.
Using these two tabs together allows you to write new guestbook entries and read the entire message history directly through Etherscan, without needing any custom frontend or development tools. This is one of the simplest and most transparent ways to interact with smart contracts on any EVM-compatible blockchain.
6. To go Further
At this point, you’ve deployed a smart contract, verified it on Etherscan, and interacted with it directly through the blockchain. This already demonstrates the core mechanics of decentralized applications: public functions, permanent data storage, and transparent state. But the real power of smart contracts comes when you connect them to a user interface. In the next post, we’ll build a simple UI using V0, complete with wallet integration, allowing users to write messages, read the guestbook, and interact with the blockchain through a clean, modern web interface instead of the Etherscan panels. This is where your guestbook begins to feel like a real application.
There are also many ways you can expand the GoldenBook contract itself. You could transform messages into Proof-of-Attendance (POA) NFTs for events or conferences, turning each signature in the guestbook into a collectible token. You could add optional tips, allowing users to attach small amounts of ETH to messages. Or you might include moderation features, message reactions, or event-based unlocks. Solidity gives you full control over on-chain logic, and because the contract is deployed on an EVM-compatible chain, these features will work across the entire Ethereum ecosystem.
It’s worth noting that blockchain and smart contracts also open compelling possibilities for IoT-driven city systems. Sensors can submit environmental data, mobility information, or infrastructure events directly to a secure, tamper-resistant ledger—similar to how our guestbook stores messages. Combined with decentralized identity, multi-sensor validation, or token-based incentives, this approach could support transparent reporting, urban monitoring, or community-driven data collection. Today’s simple guestbook is just a first step, but it illustrates the fundamental mechanism behind many emerging decentralized IoT and smart-city applications.
In the next article, we’ll bring this project to life with a user-friendly interface and wallet connection so anyone can write their message on-chain with a single click.
Table of contents


Leave A Comment